India’s industrial sector, consuming 51% of the nation’s energy and generating 31% of energy-related emissions, presents a critical decarbonization challenge through its heating requirements. While green hydrogen offers promise, the path to sustainable industrial heating requires a strategic assessment of multiple solutions – from bio-derived fuels to electric heating systems and thermal storage. Success lies in understanding how these technologies can complement each other based on their efficiency, maturity, and implementation feasibility.
India’s industrial sector is a major contributor to country’s energy demand and significantly influences the country’s carbon emissions profile. In 2021-22, the industrial sector accounted for ~51% of India’s total energy consumption1. The energy consumed for heating purposes constitutes a significant portion of total industrial energy demand which, in turn, contributes to the emissions problem as well.
According to the International Energy Agency, in India, the industrial sector is responsible for about 31% of energy-related CO2 emissions2. With diverse heating requirements across industries, the choice of heating sources plays a crucial role in shaping their energy use and environmental impact.
Unlocking low-carbon industrial heating demands a holistic view beyond green hydrogen’s promise. While green hydrogen offers transformative potential, businesses must weigh its advantages alongside other alternative solutions – from bio-derived fuels to advanced industrial electric heating systems and thermal storage innovations. Only by examining the full spectrum of emerging technologies through the lens of efficiency, maturity and implementation challenges can we get a clearer view on the role of green hydrogen.
Industrial heating: Energy demand in key sectors
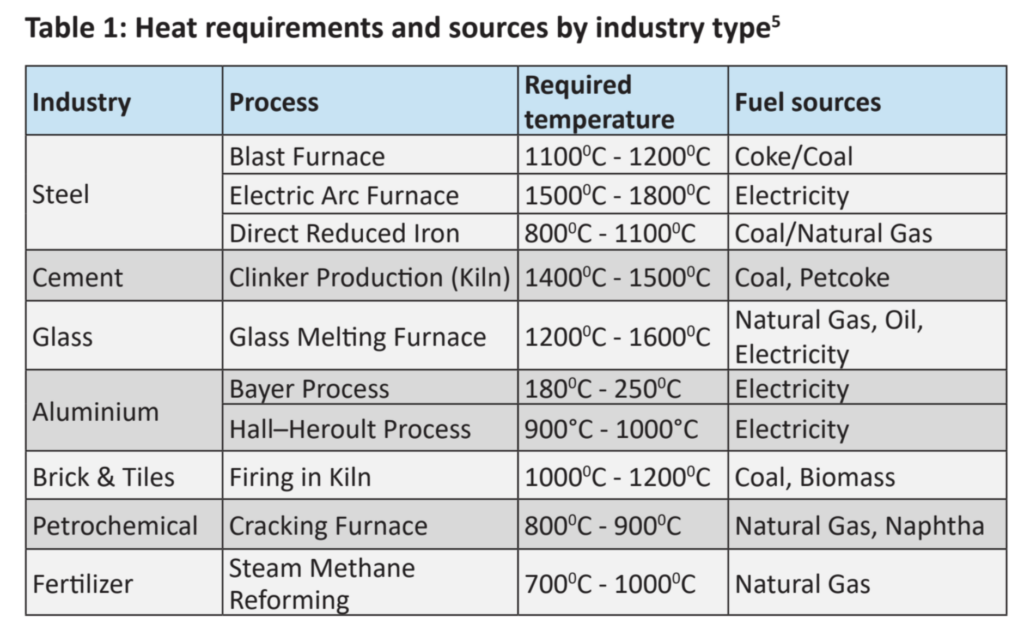
Sectors such as steel, cement, and glass manufacturing often require high temperatures (>500°C) and primarily rely on coal, natural gas, furnace oil and diesel (for redundancy)3. Meanwhile, sectors such as textiles and food processing operate at lower temperatures (up to 500°C), utilising steam generated from fossil fuels4.
Table 1 provides an overview of some of these sectors, detailing the specific processes requiring heat.
Sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels for industrial heating applications
By reimagining industrial heating through low-carbon technologies, businesses can dramatically cut emissions while maintaining the operational excellence that drives growth. The shift to cleaner process heating technologies represents a critical step in industry’s decarbonization journey.
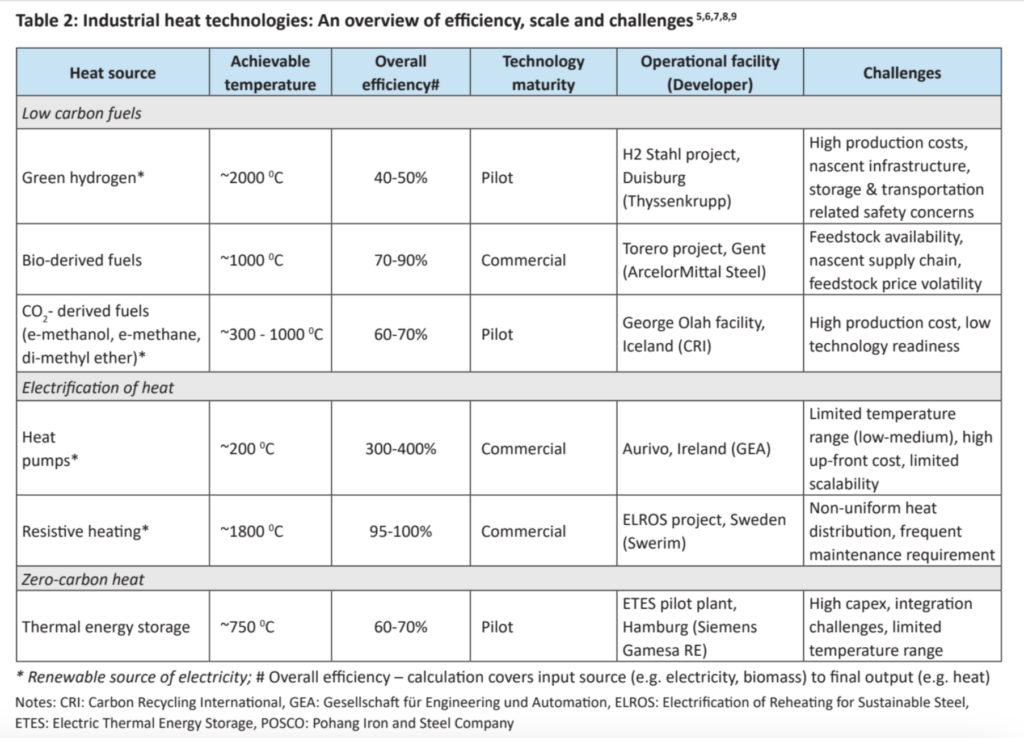
Table 2 presents a comparative analysis of different technologies including green hydrogen, aimed at decarbonizing heat production, highlighting their achievable temperatures, efficiency levels, current scale of operation, and associated challenges.
Role of green hydrogen for industrial heating applications
Powering industrial heating demand, green hydrogen can play a significant role in high-temperature processes. Yet for lower-temperature applications, electric heating technologies like heat pumps could emerge as frontrunners, delivering superior efficiency and a smaller carbon footprint.
Challenges
Despite its potential, green hydrogen adoption faces several challenges:
- Efficiency losses: Green hydrogen production, especially via electrolysis, is less efficient than direct electrification methods, such as heat pumps, which can be 4-5 times more efficient, due to energy losses at various stages of the hydrogen lifecycle.
- Cost and alternatives: For low-to-medium temperature heating, electrified solutions appear to be more cost-effective than green hydrogen-based heating. Additionally, for high-temperature heating, alternative technologies such as biofuels, geothermal, and electric heating could be more viable options, especially in regions without access to cheap renewable energy or existing gas transportation infrastructure.
- Infrastructure and scalability: Green hydrogen’s widespread adoption depends on significant advancements in production efficiency, storage, transport technologies, and infrastructure development. Without these improvements, hydrogen may remain a niche solution, particularly in regions lacking the necessary infrastructure.
Green hydrogen’s journey to transform industrial heating hinges on breakthrough advances in efficiency and scale. While poised to revolutionize sectors like petrochemicals and fertilizers, its wider adoption demands robust infrastructure and cost reductions. Success stories will likely emerge in regions blessed with abundant renewables and existing gas networks, while other markets may find their low-carbon industrial heating solutions in alternative technologies that better match their local advantages.
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364032114003104#:~:text=Conversion%20of%20solar%20energy%20into,of%20operation%20and%20simple%20maintenance.
- https://www.mospi.gov.in/sites/default/files/publication_reports/Energy_Statistics_2023/EnergyStatisticsIndia2023.pdf
- https://www.climate-transparency.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/CT2022-India-Web.pdf
- https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2023/Jun/IRENA_World_energy_transitions_outlook_2023.pdf
- https://isid4india.org/pdf/CST%20Manufacturing%20landscape%20in%20India.pdf
- https://www.agora-industry.org/fileadmin/Projects/2023/2023-20_IND_Electrification_Industrial_Heat/A-IND_329_04_Electrification_Industrial_Heat_WEB.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0375650513001120
- https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2015/IRENA-ETSAP_Tech_Brief_E05_Biomass-for-Heat-and-Power.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/d42473-022-00166-2
This article first appeared in Hydrogen India, January 2025, Vol II, Issue 5
Varun Desai
Senior Consultant, Xynteo
Bhaskar Jha
Consultant, Xynteo
For further information, follow us on social media (LinkedIn I Twitter), or Contact Us to find out how we can help your leaders and organisation create people and planet-positive impact.



